How to access SMBIOS in Windows
SMBIOS architecture
System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) is the premier standard for delivering management information via system firmware. Since its release in 1995, the widely implemented SMBIOS standard has simplified the management of more than two billion client and server systems.
For OS-present, OS-absent, and pre-OS environments, SMBIOS offers motherboard and system vendors a standard format to present management information about their products.
SMBIOS Entry Point Structure
- The only access method defined for the SMBIOS structures is a table-based method, defined in version 2.1 of SMBIOS spec
- It provides the SMBIOS structures as a packed list of data referenced by a table entry point.
- How to recognized SMBIOS Entry Point structure
- Anchor String and Intermediate Anchor String
- BYTE[0x00] — ‘SM‘(5F 53 4D 5F)
- BYTE[0x10] — ‘DMI‘(5F 44 4D 49 5F)
- Anchor String and Intermediate Anchor String
- Other information in Entry Point Structure (detail defined in spec)
- include SMBIOS version, structure table address, number of SMBIOS Structures, etc.
SMBIOS structures
Each SMBIOS structure has a formatted section and an optional unformed section. The formatted section of each structure begins with a 4-byte header.
And SMBIOS structures contains many information about the hardware platform, such as the system manufacturer or the the system BIOS version.
Structure usage guidelines (Incomplete):
- if a new field is added to an existing structure, that field is added at the end of the formatted area of that structure and the structure’s Length field is increased by the new field’s size.
- If a new field is added to an existing structure, that field is added at the end of the formatted area of that structure and the structure’s Length field is increased by the new field’s size.
- Any software that interprets a structure shall use the structure’s Length field to determine the formatted area size for the structure rather than hard-coding or deriving the Length from a structure field.
- Each structure shall be terminated by a double-null (0000h), either directly following the formatted area (if no strings are present) or directly following the last string. This includes system- and OEM-specific structures and allows upper-level software to easily traverse the structure table.
- The unformed section of the structure is used for passing variable data such as text strings
Header format of each structure
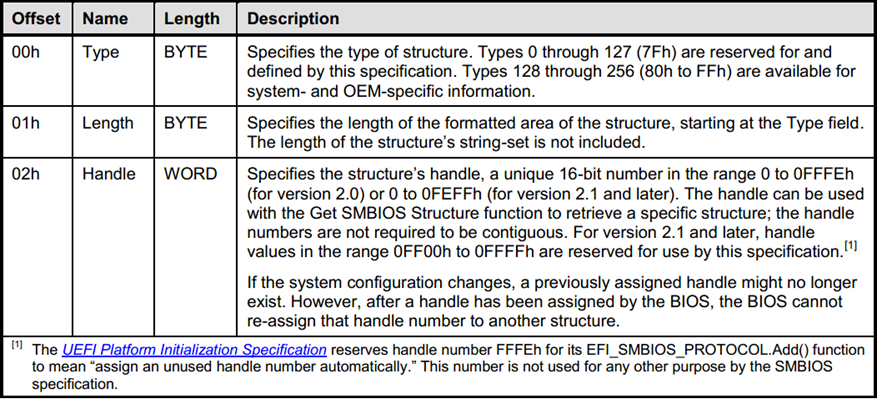
Samples of some structures
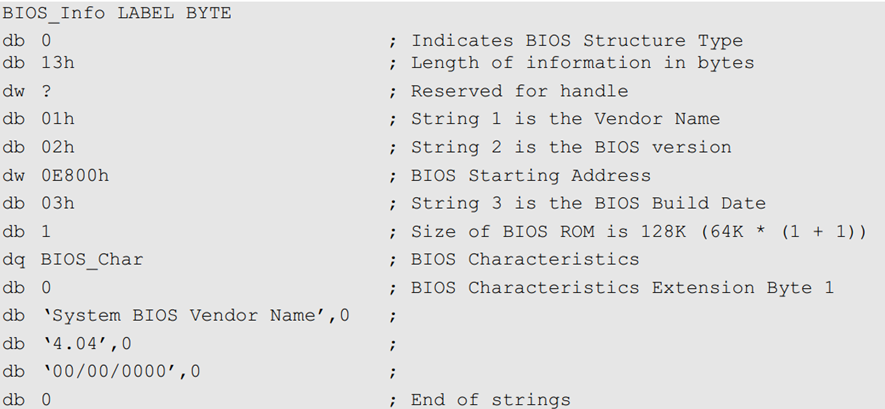
BIOS information with string
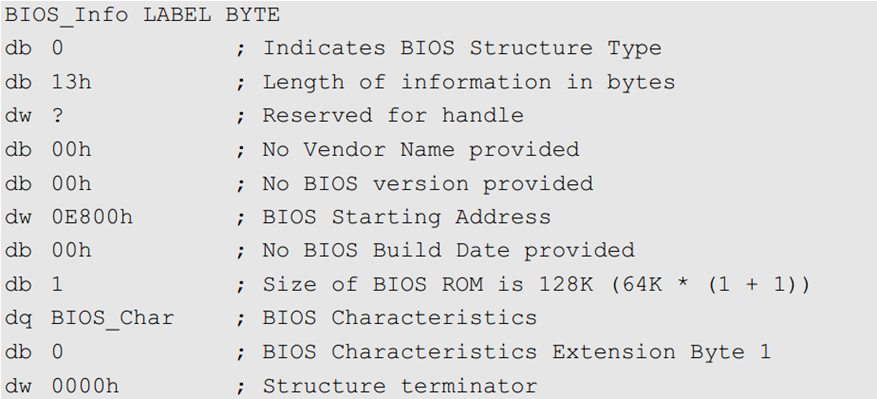
BIOS information without string
SMBIOS in Windows
Microsoft SMBIOS Driver
- Support by windows XP SP2 and later OS
- collects information and stores this information in the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Mssmbios\Data
Access SMBIOS
Different ways of access SMBIOS
- Access registry (no guarantee)
- System APIs for Reading SMBIOS Data (for applications)
- Using WMI (for drivers)
Key structure for Driver access SMBIOS
struct RawSMBIOSData
{
BYTE Used20CallingMethod;
BYTE SMBIOSMajorVersion;
BYTE SMBIOSMinorVersion;
BYTE DmiRevision;
DWORD Length; // length of SMBIOSTableData
BYTE SMBIOSTableData[]; // all smbios structures
}
The SMBIOSTableData property contains the entire SMBIOS data table, except for the SMBIOS structure table entry point.
Key APIs:
-
Application:
“EnumSystemFirmwareTables()“ and ”GetSystemFirmwareTable()”
-
Driver:
-
Windows XP and later:
“IoWmiOpenBlock()“ and the ”IoWMIQueryAllData()”
-
Windows Vista and later:
“AuxKlibGetSystemFirmwareTable()”
-
How to check SMBIOS data correct
SMBIOS Viewer — A good tool for viewing SMBIOS in windows platform.
Reference:
SMBIOS Reference Specification:https://www.dmtf.org/standards/smbios
